DeepR2OM
Introduction
2OM: RNA Stability, Translation Regulation, Splicing, mRNA Export, miRNA Binding
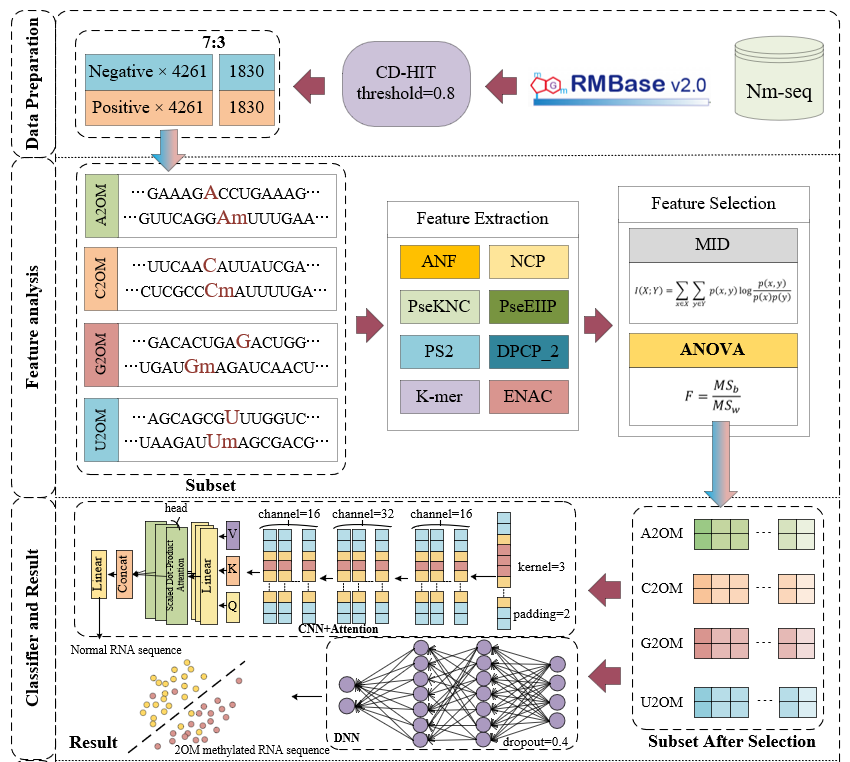
2'-O-methylation (2OM) of ribose is a widespread RNA modification that significantly impacts RNA stability, structure, and function. Accurately predicting 2OM sites is crucial for understanding RNA's biological functions and related pathologies. Traditional detection methods pose challenges such as resource intensiveness, potential RNA sample damage, and high costs. However, recent advancements in machine learning, particularly deep learning techniques, offer rapid and cost-effective prediction solutions. In this study, we introduce DeepR2OM, a novel method integrating feature selection and deep learning for 2OM sites prediction. DeepR2OM encodes sequences using eight RNA descriptors, employs feature selection algorithms to reduce dimensions, and then utilizes a deep learning network for training. After evaluating various deep learning architectures, we selected Convolutional Neural Network (CNN), Multi-Head Self-Attention mechanism, and Deep Neural Network (DNN) as our final prediction models. Experimental results demonstrate DeepR2OM's effectiveness, achieving 87.1% accuracy (ACC), 85.5% recall rate (Recall), 87.9% precision (PRE), and a Matthews correlation coefficient (MCC) of 75.7% on an independent test set. This tool serves as a valuable resource for exploring the functional and bioinformatic aspects of 2OM sites.